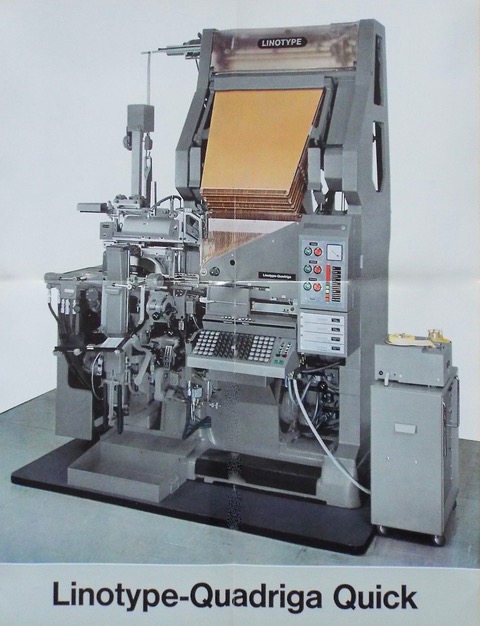
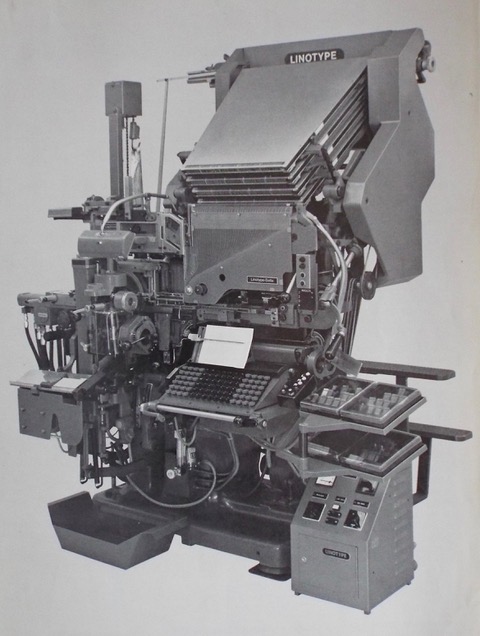
This machine was the German version of the English Model 79 or the American Comet—a high speed model capable of casting 15 newspaper-measure lines per minute when working on tape. It could also be operated manually, when the casting rate could be stepped-down to take account of the fact that not many operators were capable of working at such a high speed and thus there was no valid reason for the machine to be subjected to such wear and tear when there was no call for it. Slowest casting speed was 10 lines per minute.
Unlike its American and English forebears, the Quadriga was equipped with four 90-channel magazines and these were sloped at the steeper 54-degree angle common to all three machines, ensuring that the mats did not hang around once summoned from the keyboard. There was no mixing facility, as the machine was intended as a fast straight text-setter. Hydraquadder and Mohr saw were obtainable as extras; the former would be fairly essential in both manual and tape-operated state, whereas the saw would really only be needed if manual operation was envisaged. The knifeblock could deal with slugs up to 42pt, which again was a feature not needed if tape operation was chosen.